
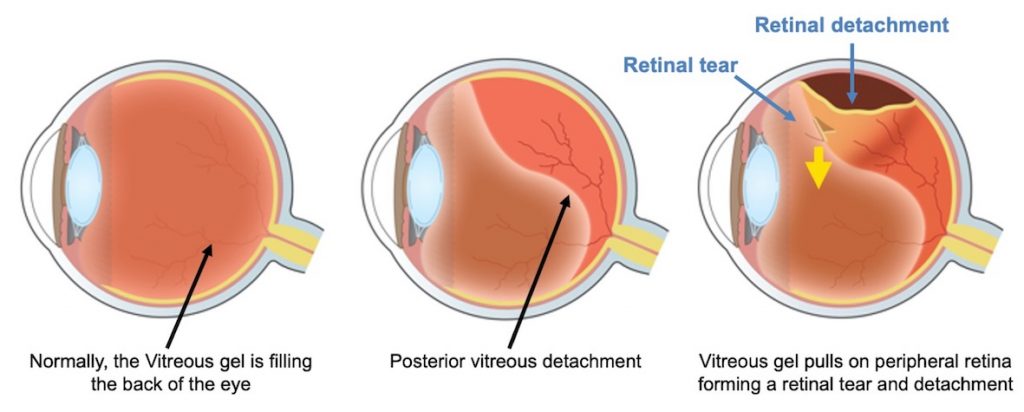
On rare occasions, a detached retina may occur after LASIK surgery in highly short sighted people. This is because highly short sighted people typically have longer-than-normal eyeballs with thinner retinas that are more prone to detaching. High levels of short sightedness also can cause a retinal detachment. What causes a retinal detachment?Īn injury to the eye or face can cause a detached retina. Urgent treatment increases your odds of regaining lost vision. If you experience any of the visual signs of retinal detachment, consult you optician immediately. And 50 percent of people who have a retinal tear will experience a subsequent retinal detachment.Ī detached retina is painless. These signs can occur gradually as the retina pulls away from the supportive tissue, or they may occur suddenly if the retina detaches immediately.Īpproximately one in seven people who experience a sudden onset of flashes and floaters will have a retinal tear or detachment. (The use of silicone oil is usually reserved for complex retinal detachments such as those with associated scar tissue or very large retinal tears.Seeing a curtain-like shadow coming down across your field of vision can be a sign of retinal detachment.Īnother sign is seeing a shadow or a curtain descending from the top of the eye or across from the side. Silicone oil may be removed at a later date with another vitrectomy. Gas goes away slowly on its own, but oil does not. Lastly, the eye is filled with either gas or silicone oil. Laser is then used to seal the retinal tears. As the name implies, it involves surgical removal of the vitreous gel which, in turn, relieves the traction or pulling on the retinal tear that is causing the detachment. Vitrectomy surgery is also performed in the operating room. In some cases, a scleral buckle may be combined with vitrectomy surgery. A gas bubble is sometimes used to facilitate reattachment of the retina. It is coupled with either cryotherapy or laser photocoagulation.

It consists of suturing a soft piece of silicone to the eye wall (sclera) in such a way as to gently indent the sclera in order to support and close the retinal tear. Scleral buckle surgery is performed in the operating room. After the procedure, patients must maintain a specific head position for about a week to ensure that the retinal tear is adequately sealed The gas injection is coupled with either a freezing treatment (cryotherapy) or laser photocoagulation to permanently seal the causative retinal tear. It involves the injection of a temporary gas bubble to close the retinal tear and surrounding detachment. Pneumatic Retinopexy is an office-based procedure. The choice of treatment depends on certain features of the detachment such as number and location of retinal tears as well as patient characteristics such as age and past cataract surgery. There are three approaches to repairing a retinal detachment: However, if a retinal detachment has already developed, a retinal reattachment procedure is typically necessary. If a retinal hole or tear is detected before there is retinal detachment, laser or cryotherapy (freezing treatment) to the retinal tear is often successful in sealing the retinal defect, preventing a retinal detachment.
CAUSES AND SYMPTOMS OF DETACHED RETINA HOW TO
Treatment and How to Prevent Retinal Detachment Longstanding retinal detachments or those with associated scar tissue (proliferative vitreoretinopathy) typically have a poor visual prognosis.
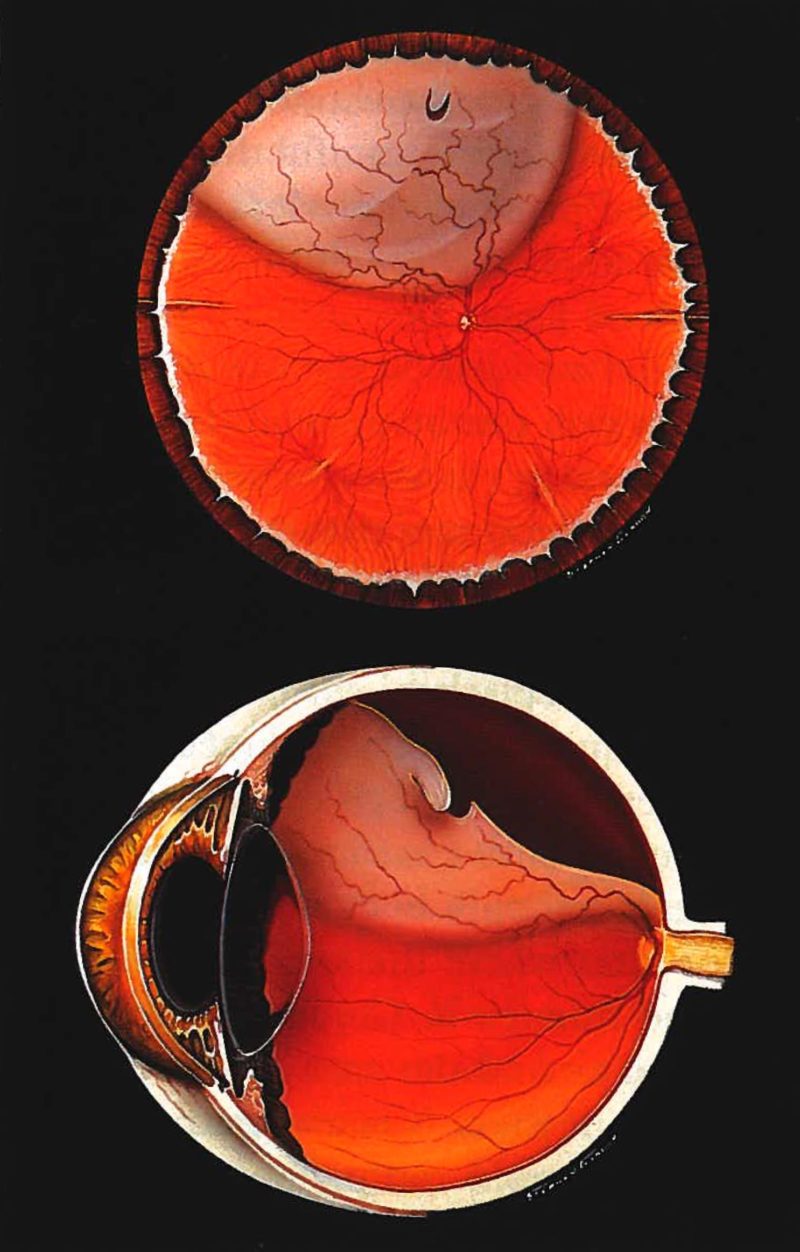
A change of eyeglasses after retinal detachment surgery may or may not improve vision. Final visual outcomes are best if the detachment is detected and treated before it involves the center of the retina (macula). Retinal detachments often cause some degree of permanent visual field or central visual acuity loss, even after successful reattachment. There may also be some degree of vitreous hemorrhage, which occurs when a retinal tear involves a retinal blood vessel. Through a dilated pupil, the ophthalmologist will see one or more tears in the retina with varying amounts of underlying fluid. A comprehensive ophthalmic examination is essential to diagnose and treat a retinal detachment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
